[ad_1]
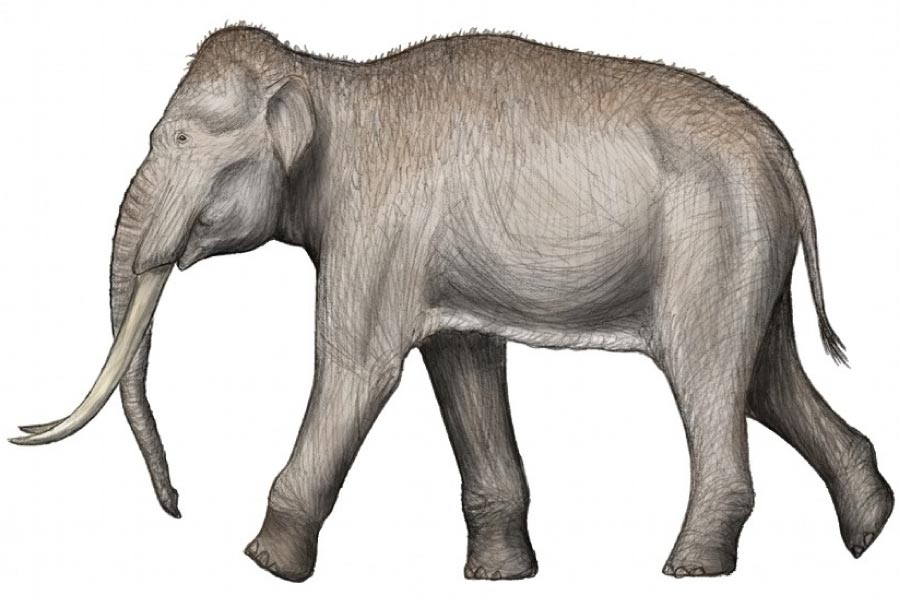
The straight-tusked elephant was one of many largest land mammals that ever lived. The extinct species, which was considerably larger than at this time’s African bush elephant (pictured above), lived alongside Neanderthals in prehistoric Germany, round 125,000 years in the past.
A current evaluation of fossilized straight-tusked elephant bones reveals the connection between the prehistoric species and its early human hunters.
Associated Pages
Analysis Findings
Located close to Halle in Germany is the Center Paleolithic archaeological website Neumark-Nord. Among the many 1000’s of Pleistocene artifacts and fossils which have been recovered from the positioning are the stays of not less than 57 straight-tusked elephants – the biggest gathering of the species but found.
The elephants have been represented by over three thousand separate fossils, with some elephants being discovered almost full, and others being discovered scattered over numerous places.
The elephants would have lived round 125,000 years in the past, in the course of the final interglacial – a interval of heat earlier than the Arctic polar ice sheets would as soon as once more broaden to cowl a lot of the Northern Hemisphere.
Earlier analysis had revealed that almost the entire straight-tusked elephants discovered at Neumark-Nord have been adults, and most have been males.
That is an uncommon grouping, each in fossilized and dwelling elephants. Often, it’s grownup females and infants that dwell in herds, with grownup males tending to be extra impartial.
Lately, a group of scientists re-examined the elephant fossils, and located proof which may clarify this inconsistency. They printed their findings in this report.
The group discovered that lots of the fossils have been marked by cuts doubtless attributable to the stone instruments of early people. This confirmed that the elephants had been hunted, and ready for consumption, by the Neanderthals identified to reside within the space on the time.
This may clarify the bizarre male / feminine and age ratios of the fossilized elephants; the Neanderthals are thought to have focused male elephants, due each to their larger measurement and the truth that they have been solitary, which can have made them simpler to seize.
A possible looking technique would have been to drive the large animals into the muddy shore of a lake. Right here the elephant would tire, permitting it to be subdued with spears.
It isn’t simply the looking of the elephants that might have required the cooperation of a big variety of people; making ready the animal’s meat for consumption would even have required a substantial quantity of labor, even when shared amongst quite a few people.
It’s calculated {that a} single male straight-tusked elephant would have been in a position to present the each day dietary necessities of not less than 2,500 Neanderthals.
The sheer quantity of meals, along with the labor required to hunt and course of a single elephant, means that Neanderthals lived or congregated in teams a lot bigger than beforehand thought, and/or they’d the means to protect meals.
Neanderthals have been beforehand thought to have lived in teams of as much as 20 people. The brand new analysis means that they fashioned bigger congregations – ether short-term or everlasting – with a view to hunt and put together elephants.
Straight-Tusked Elephant
The straight-tusked elephant is a long-extinct member of the elephant household, Elephantidae. It lived in Europe and western Asia from round 800,000 to 100,000 years in the past, in the course of the Pleistocene epoch.
The prehistoric elephant was an infinite animal, standing as much as 4.2 m / 13.78 ft tall and weighing as much as 15 metric tonnes.
That’s considerably larger than at this time’s African bush elephant – the biggest dwelling land animal – which stands a most 3.96 m / 13 ft. tall and weighs as much as 10.4 metric tonnes.
Though enormous, the straight-tusked elephant wasn’t the biggest elephant that ever lived – that accolade goes to its shut relative, the Asian straight-tusked elephant Palaeoloxodon namadicus.
The Pleistocene Epoch
The Pleistocene epoch is a part of the Quaternary Interval – the time frame wherein we presently dwell. It started round 2.58 million years in the past, and ended round 11,700 years in the past. The Pleistocene was adopted by the Holocene epoch, the present epoch.
The Pleistocene was an ice age – a interval marked by a cycle of chilly intervals, or “glacials”, and hotter intervals, or “interglacials”. The vary of the straight-tusked elephant doubtless grew and shrank as interglacials got here and went.
Neanderthals
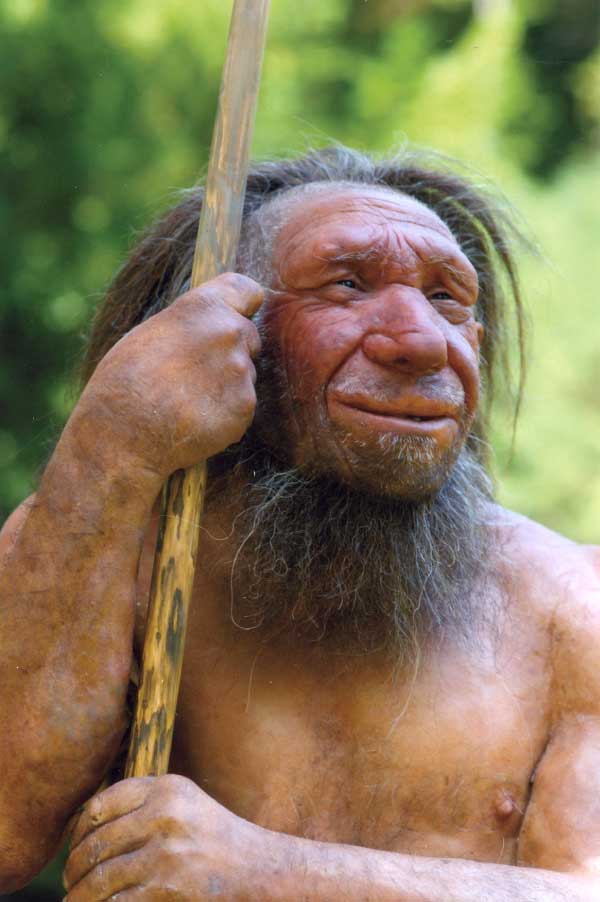

Additionally inhabiting Europe in the course of the Pleistocene have been Neanderthals – hominids (member of the good ape household, Hominidae) carefully associated to people.
Neanderthals have been barely shorter than the common fashionable human, however have been powerfully constructed, and certain extremely smart – their mind circumstances have been considerably bigger than ours.
Neanderthals lived onerous, bodily demanding lives, with the vast majority of identified specimens exhibiting indicators of having been injured, usually severely, in some unspecified time in the future of their lives.
Many Neanderthal accidents have been attributable to animal assaults, with bears, massive cats and wolves being the principle culprits. Just like the fearsome cave bears and cave lions of the time, Neanderthals lived in caves, which is probably one purpose why accidents from animals are so frequent.
Neanderthals used instruments, and will create fireplace and make easy garments. They even used primitive medicines.
Neanderthals have been apex predators that hunted a wide range of animals. Deer are thought to have been the early people’ most typical quarry, however animals resembling goats, cattle, bears, birds, rhinos, mammoths – and elephants, have been additionally taken.
Like fashionable people, Neanderthals have been omnivores that additionally ate vegetation and fungi.
Uncover Extra With Energetic Wild
[ad_2]
